
- #Determine ip and mac header information for a data packet Pc
- #Determine ip and mac header information for a data packet windows
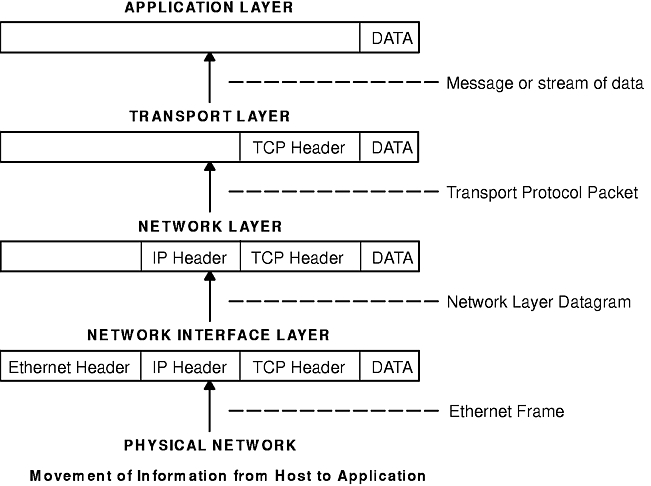
Is the source MAC address the same as the one recorded from Part 1 for the local PC? _ The destination MAC address is from the default gateway because this is the last stop before this query exits the local network.
#Determine ip and mac header information for a data packet Pc
The source MAC address is from your local PC because your local PC originated the DNS query. The Ethernet II line displays the source and destination MAC addresses.This is the number of bytes to send a DNS query to a name server requesting the IP addresses of In the first line in the packet details pane, frame 15 had 74 bytes of data on the wire.The protocol entries are highlighted in gray. The protocols in this query are displayed in the packet details pane (middle section) of the main window. In this example, Wireshark capture frame 15 in the packet list pane is selected for analysis. Step 2: Examine a UDP segment using DNS query.Įxamine the UDP by using a DNS query for as captured by Wireshark. In the packet list pane (top section) of the main window, locate the packet that includes Standard query and A See frame 15 as an example.If this does not resolve the issue, type nslookup in the command prompt window as an alternative to the web browser. Restart the Wireshark capture and repeat the instructions in Part 2b –2e. In the command prompt window, type ipconfig /flushdns to remove all previous DNS results. Note: If you do not see any results after the DNS filter was applied, close the web browser. In the Wireshark main window, type dns in the entry area of the Filter toolbar and press Enter.In Part 3, you will examine the UDP packets that were generated when communicating with a DNS server for the IP addresses for Step 1: Filter DNS packets.

Part 3: Analyze Captured DNS or UDP Packets

Click Stop to stop the Wireshark capture when you see the Google home page.Open a web browser and type Press Enter to continue.
After selecting the desired interface, click Start to capture the packets.Select (highlight) the active capturing interface. Select an interface for Wireshark to capture packets.
#Determine ip and mac header information for a data packet windows


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
